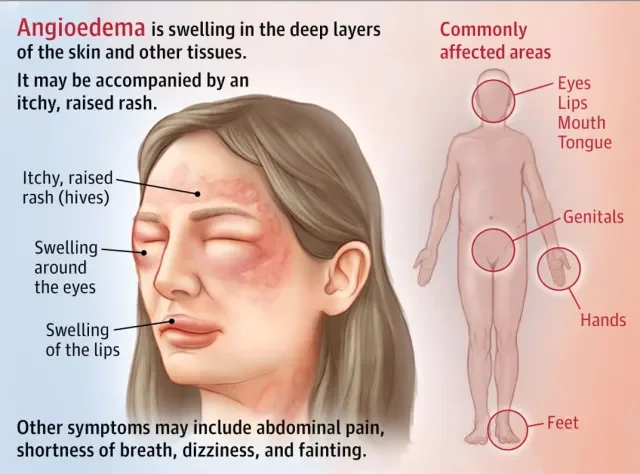
Deep skin swelling also known as subcutaneous swelling can be a painful and alarming symptom. It often indicates an underlying issue such as infection, inflammation, allergic reaction, or trauma. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
What Is Deep Skin Swelling?
Deep skin swelling occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues beneath the skin. This can happen due to:
-
Bacterial infections (e.g., cellulitis or abscesses)
-
Inflammatory conditions (e.g., lupus, vasculitis)
-
Allergic reactions
-
Injury or trauma
-
Autoimmune diseases
The swelling may present with redness, warmth, pain, and restricted movement in the affected area. It may be localized or spread across a larger region, depending on the cause.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Bacterial Infection
One of the most common causes of deep skin swelling is a bacterial infection, particularly cellulitis. This condition involves the deep layers of skin and underlying tissue and is typically caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria.
Signs include:
-
Warmth and tenderness
-
Rapid swelling
-
Fever and chills
-
Pus or drainage (in case of abscess)
If untreated, cellulitis can lead to serious complications, including sepsis.
2. Trauma and Injury
Blunt force trauma, fractures, or puncture wounds can damage tissues and blood vessels, causing fluid buildup. Swelling from injury is usually immediate and accompanied by bruising.
3. Allergic Reactions
Allergies to medications, insect bites, or certain foods can cause swelling through histamine release. This is often seen in angioedema, where swelling occurs around the eyes, lips, and throat.
4. Autoimmune Conditions
Diseases like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or dermatomyositis can cause swelling due to chronic inflammation of the skin and underlying tissues.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider will assess your symptoms and medical history. Diagnostic methods may include:
-
Physical examination for redness, heat, and tenderness
-
Blood tests to check for infection or autoimmune markers
-
Ultrasound or MRI to evaluate fluid buildup or abscess formation
-
Skin or wound cultures to identify bacterial strains
Treatment Options
Treatment for deep skin swelling depends on the underlying cause:
1. Antibiotics for Bacterial Infections
If the swelling is due to a bacterial infection like cellulitis or an abscess, oral or intravenous antibiotics are the first line of defense. Cephalexin, a first-generation cephalosporin, is often prescribed due to its efficacy against skin pathogens.
Finding a reliable cephalexin capsules supplier is critical, especially for healthcare facilities or pharmacies that need to maintain consistent inventory. A trusted supplier ensures quality, proper storage, and timely delivery factors essential to patient care and treatment effectiveness.
2. Drainage of Abscesses
When pus collects under the skin, it forms an abscess. Antibiotics alone may not be sufficient. In such cases, a minor surgical procedure is performed to drain the pus and relieve pressure.
3. Anti-inflammatory Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen may help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. For autoimmune-related swelling, corticosteroids or disease-modifying drugs may be prescribed.
4. Allergy Treatment
For allergic reactions, antihistamines or corticosteroids are used. In severe cases like anaphylaxis, an epinephrine injection may be required.
5. Cold Compresses and Elevation
For minor swelling due to injury or strain, apply a cold compress to reduce inflammation. Elevate the affected limb to encourage drainage of excess fluid.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Deep skin swelling can escalate rapidly. Seek immediate medical help if you notice:
-
Rapid increase in swelling
-
Spreading redness or red streaks
-
Fever, chills, or nausea
-
Difficulty moving the affected area
-
Signs of an allergic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, throat tightness)
Prevention Tips
While not all causes of deep skin swelling are preventable, here are some tips to reduce your risk:
-
Practice good hygiene to prevent skin infections.
-
Treat wounds promptly, cleaning and covering them to avoid contamination.
-
Wear protective gear during activities that could cause trauma.
-
Manage chronic conditions like diabetes, which increase infection risk.
-
Identify and avoid allergens if you have known sensitivities.
Choosing the Right Cephalexin Capsules Supplier
For healthcare providers and pharmacists, partnering with a dependable cephalexin capsules supplier is crucial. Look for a supplier that offers:
-
Regulatory compliance with FDA or equivalent health authorities
-
Batch testing and quality assurance
-
Fast and reliable delivery services
-
Transparent sourcing and manufacturing practices
-
Good customer support
A consistent and trustworthy supplier not only supports better patient outcomes but also helps prevent medication shortages in critical situations.
Final Thoughts
Deep skin swelling is more than just a cosmetic concern it can signal serious underlying health issues. Timely diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications. In cases caused by bacterial infections like cellulitis, medications such as cephalexin play a vital role in recovery.
Whether you’re a patient seeking effective treatment or a medical professional managing inventory, access to high-quality antibiotics is essential. Partnering with a reputable cephalexin capsules supplier ensures that treatment is both timely and effective helping patients recover faster and reducing the risk of long-term damage.