Introduction
Impregnating resins play a crucial role in enhancing the performance and reliability of electrical components, especially in high-stress industrial applications. As the world increasingly embraces electric vehicles, renewable energy, and modern infrastructure, the demand for advanced insulation and protection technologies continues to rise driving robust growth in the impregnating resins market.
Market Size and Forecast
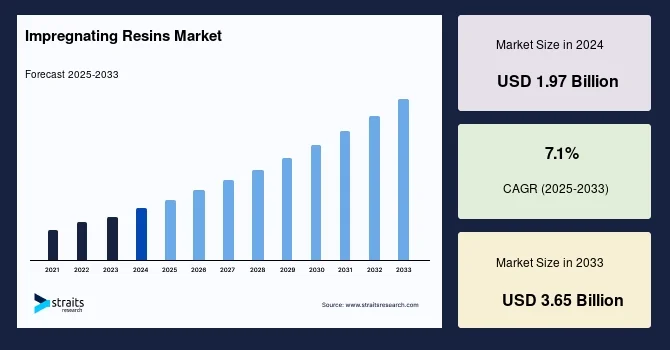
According to Straits Research, the global impregnating resins market was estimated at USD 1.97 billion in 2024. It is projected to grow to USD 2.11 billion in 2025 and reach USD 3.65 billion by 2033, exhibiting a CAGR of 7.1% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
This impressive growth reflects the increasing global demand for energy-efficient, long-lasting electrical equipment and insulation systems. Key contributing sectors include electric vehicles, renewable energy, electronics manufacturing, and smart grid infrastructure.
What is Impregnation Material?
Impregnation material refers to any substance typically a liquid used to fill the voids within porous materials or components. These materials penetrate the microscopic gaps and crevices in substrates such as coils, windings, or laminates, enhancing their structural integrity, durability, and resistance to moisture, heat, and chemicals.
What is Impregnation Resin?
Impregnation resin is a specialized type of impregnation material. It is a low-viscosity liquid resin formulated to deeply penetrate insulating components and windings in electrical equipment. Once cured (usually through heat or UV light), the resin solidifies, providing mechanical strength, electrical insulation, thermal stability, and environmental protection.
Common types of impregnation resins include:
-
Epoxy resins – known for superior mechanical and thermal properties.
-
Polyester resins – widely used due to their cost-effectiveness and fast curing.
-
Polyurethane resins – offering flexibility and chemical resistance.
-
Polyesterimide resins – used for high-temperature applications.
What is Impregnation Treatment?
Impregnation treatment is the industrial process of applying impregnation resins to components, typically using methods such as vacuum impregnation, pressure impregnation, or trickle impregnation. This treatment ensures complete resin infiltration into internal structures, preventing air gaps, increasing dielectric strength, and extending the lifespan of components like motors, transformers, and generators.
Key Market Drivers
-
Electric Vehicles (EVs):
EV powertrains rely heavily on electrical motors and components that require high-grade insulation and heat resistance. Impregnating resins are vital for improving motor efficiency and durability, making them indispensable in EV production. -
Renewable Energy Expansion:
Wind turbines, solar inverters, and hydropower generators all use components that must withstand extreme environmental conditions. Impregnating resins provide the thermal and mechanical stability needed in these demanding environments. -
Growth of the Electronics Sector:
As the miniaturization of electronics continues, impregnating resins are increasingly used to protect micro-components from vibration, moisture, and overheating especially in smart devices and industrial electronics. -
Aging Power Infrastructure:
Many countries are modernizing outdated electrical grids. Upgrading transformers and generators involves the use of advanced resins to ensure long-term reliability and reduce energy losses.
Types of Impregnating Resins
-
Solvent-Based Resins: Known for high penetration ability, but less environmentally friendly due to solvent emissions.
-
Solventless Resins (100% solids): Environmentally preferred due to zero VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds), offering excellent performance in demanding applications.
-
Water-Based Resins: Gaining popularity due to eco-friendliness and ease of handling.
Regional Insights
-
North America currently dominates the market, accounting for the largest revenue share. This is due to the presence of advanced industries, robust automotive manufacturing, and stringent regulatory frameworks that promote high-performance insulation technologies.
-
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, fueled by rapid industrialization, increasing investments in renewable energy, and a booming electric vehicle market in countries like China, India, and Japan.
Major Industry Applications
-
Motors and Generators – To enhance heat resistance, mechanical strength, and lifespan.
-
Transformers – For improved insulation and reduced energy losses.
-
Automotive Electronics – Protecting control systems, sensors, and power electronics.
-
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) – To safeguard against corrosion, dust, and thermal shock.
-
Household Appliances – Ensuring long-term performance of components like compressors and pumps.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the impregnating resins market is poised for strong growth, it also faces some challenges, such as:
-
Environmental regulations concerning the use of solvent-based resins.
-
High cost of certain advanced resin formulations.
-
Need for specialized equipment and expertise in resin application processes.
However, these challenges also open up new opportunities, particularly in the development of eco-friendly, low-VOC resins, and automated impregnation technologies that reduce human error and improve efficiency.
Conclusion
The impregnating resins market is undergoing a transformative phase, driven by innovation, sustainability trends, and the growing need for high-performance electrical insulation systems. With a projected market size of USD 3.65 billion by 2033 and a steady CAGR of 7.1%, the future of this industry looks promising.