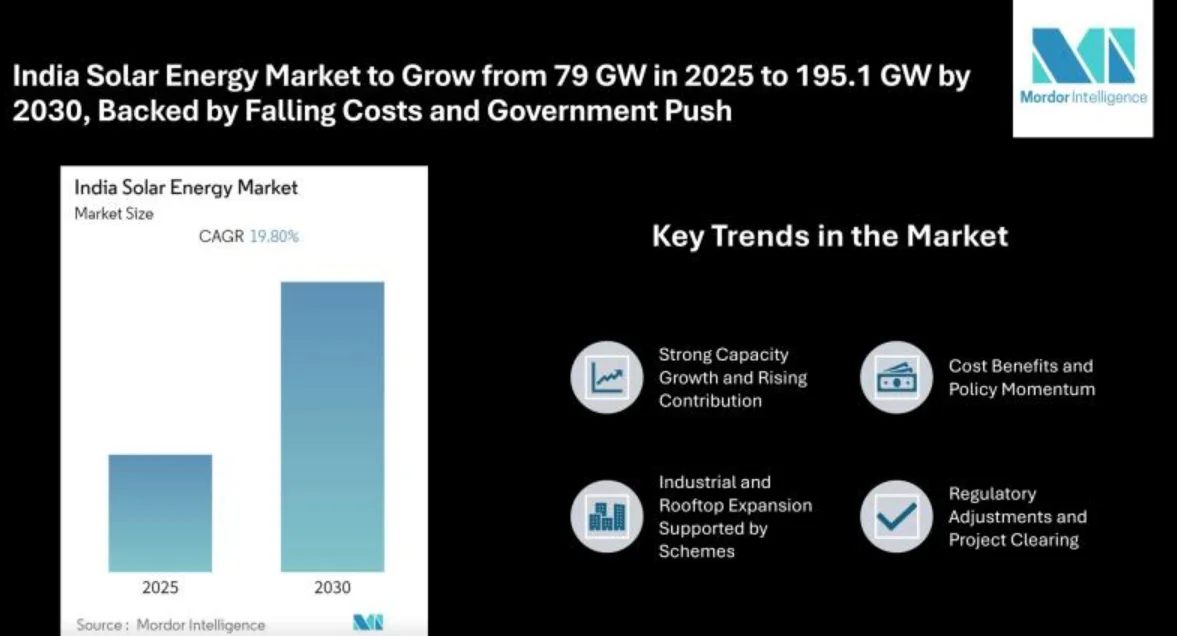
India's solar energy sector is poised for sharp growth in the years ahead. According to Mordor Intelligence, the country's installed solar capacity stands at 79.07 gigawatts (GW) as of 2025, with projections pointing to a rise to 195.11 GW by around 2030, representing a strong compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 19.8%. This surge reflects both the country's rich sunny terrain and policies encouraging solar deployment.
Beyond capacity growth, India's solar output is already reshaping electricity generation patterns. From January to April 2025, solar generation jumped 32.4% year‐on‐year, reaching 57.8 terawatt-hours (TWh), and pushed solar's share of the power mix to 10% in March-April. At the same time, coal and gas-fired generation eased back, marking a subtle but significant shift in energy sources.
Top Key Trends
Strong Capacity Growth and Rising Contribution
The climb from ~79 GW to ~195 GW signals a sharp climb in solar infrastructure. Meanwhile, clean energy additions are reducing fossil fuel reliance — India’s solar generation outpaced the decline in coal-fired output earlier in 2025.
Cost Benefits and Policy Momentum
Solar power has become notably more competitive — significantly cheaper than new coal capacity. This cost advantage, paired with government schemes and international investment, is reinforcing solar's push across households and large projects alike.
Industrial and Rooftop Expansion Supported by Schemes
The Pradhan Mantri Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, launched in February 2024, aims to bring rooftop solar to 1 crore households, offering free electricity up to 300 units per month and substantial subsidies for installation. Gujarat has taken an early lead with over 336,000 rooftop systems in place and over 1,200 MW capacity added.
Regulatory Adjustments and Project Clearing
To address delays and project backlog, India recently scrapped its central renewable energy pricing pools (implemented in 2024), aiming to unclog stalled installations and accelerate power purchase agreements.
Challenges Around Grid and Storage
While solar generation is surging, grid integration and storage lag behind. Issues such as surplus daytime rooftop solar in Kerala are leading to financial strain on utilities and billing challenges. This highlights the gap between generation growth and system readiness.
Market Segmentation
India's solar landscape is structured across several segments, including those highlighted in related photovoltaic market data:
By System Type
- Utility‐scale installations, like large solar farms (e.g., Bhadla Solar Park), are key anchors of capacity.
- Rooftop systems, spanning residential and commercial customers, are ramping up through schemes like Surya Ghar and corporate contracts.
By Deployment Type
- Ground‐mounted projects form the bulk of utility‐scale growth.
- Rooftop PV is rising fast, with rooftop solar markets growing at a CAGR of ~18.7% between 2024 and 2029.
By End‐User Segment (For Photovoltaic Market)
- Residential — households adopting small-scale solar.
- Commercial & Industrial (C&I) — businesses and factories.
- Utility — large grid-connected power producers.
Regional / Project Highlights
Bhadla Solar Park in Rajasthan, with a capacity of 2,245 MW, remains India's largest solar facility, contributing significantly to overall capacity.
Top Key Players
Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd — a leading rooftop EPC player, known for projects like the large-scale solar rooftop at the Mumbai cricket stadium.
Vikram Solar — a major module manufacturer with about 4.5 GW capacity, plus a growing EPC footprint, involved in large ground-mounted and airport projects.
Emmvee Group — another Bengaluru-based PV module maker, with around 6.6 GW module and 2.5 GW cell manufacturing capacity as of early 2025 — expanding fast and known for reliability testing.
Other significant players in the photovoltaic segment include Adani Group, Azure Power, and Mahindra Susten, reflecting a competitive field across large-scale and rooftop solar.
At Mordor Intelligence, we go beyond numbers to offer a clear perspective on the forces shaping global markets. Our research highlights the technologies, consumer shifts, and industry dynamics that matter most, giving business leaders the insights they need to make informed decisions.
The india solar energy market analysis goes beyond basic data, offering clarity on competitor moves, product pipelines, and evolving trends. This perspective helps businesses anticipate change, capture growth, and build a stronger market presence.
Conclusion
This expansion is driven by falling solar costs, government support programs that ease adoption, and growing clean energy goals. Solar generation is already helping curb fossil fuel use, with a notable jump early in 2025.
But the journey ahead is not without challenges. Grid integration, storage capacity, and bureaucratic or financial hurdles — for both utility-scale projects and rooftop systems — must be addressed. Moves like scrapping central pricing pools aim to unclog stalled deals, while schemes like Surya Ghar are unlocking consumer adoption.