Modern flooring solutions are no longer judged by appearance alone. Performance, durability, safety, and long-term maintenance have become equally important across industrial, commercial, and residential environments. From manufacturing plants and laboratories to warehouses and modern homes, flooring systems must withstand mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and environmental changes.
Among high-performance flooring options, epoxy flooring stands out due to its advanced chemical composition. Unlike conventional surface finishes, epoxy flooring systems are engineered using carefully formulated chemical components that create a seamless, durable, and highly resistant surface. The chemical structure of epoxy directly influences its strength, adhesion, and lifespan.
As demand grows for reliable flooring solutions that balance performance and affordability, understanding the chemistry behind epoxy flooring becomes essential. This article explores how chemical composition defines epoxy flooring performance without referencing any specific brand.
What Is Epoxy Flooring? A Chemical Perspective
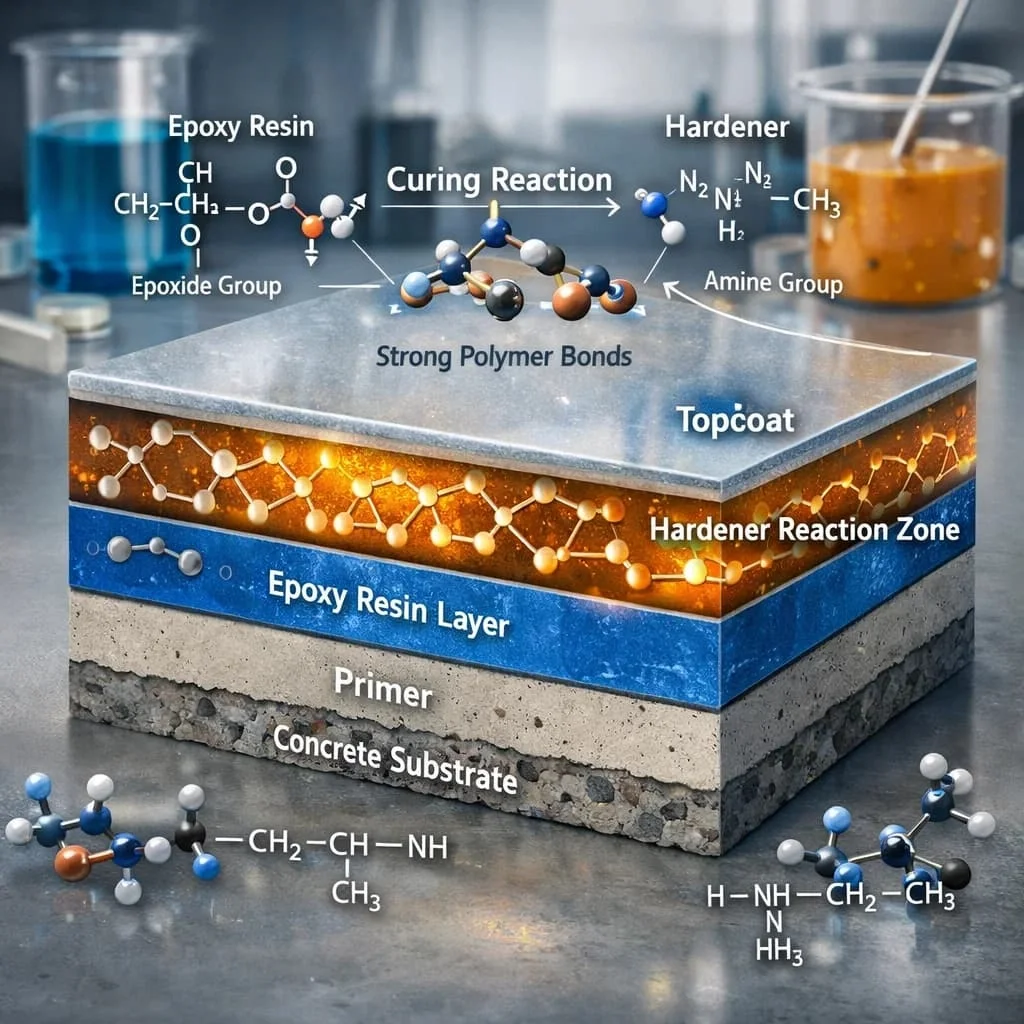
From a materials science viewpoint, epoxy flooring is a thermosetting polymer-based system created through a chemical reaction between resin and a curing agent. Unlike simple surface coatings that sit on top of concrete, epoxy flooring forms a chemically bonded layer that integrates with the substrate.
The core strength of epoxy flooring lies in polymer chemistry. Polymers form long molecular chains that interlink during curing, creating a dense, cross-linked structure. This chemical bonding gives epoxy flooring its characteristic hardness, chemical resistance, and durability.
Understanding epoxy flooring at a chemical level explains why it performs better than traditional cementitious or paint-based systems. The formulation is not just decorative—it is engineered to deliver long-term structural and functional benefits in demanding environments.
Core Chemical Components of Epoxy Flooring
Epoxy flooring systems consist of two primary chemical components that work together to form a solid, durable surface.
The first component is epoxy resin, a reactive polymer containing epoxide groups. These groups are responsible for forming strong chemical bonds during curing. The second component is the hardener, also known as the curing agent, which initiates and controls the polymerization process.
When mixed in precise proportions, the resin and hardener undergo a chemical reaction known as cross-linking. This reaction transforms the liquid mixture into a rigid, three-dimensional polymer network. The resulting structure is seamless, non-porous, and mechanically strong.
This molecular-level bonding is what allows epoxy flooring to resist moisture penetration, mechanical wear, and chemical exposure, making it suitable for a wide range of demanding applications.
Role of Epoxy Resins in Flooring Performance
The chemical structure of epoxy resins plays a critical role in flooring performance. Epoxy resins are designed with reactive sites that enable strong adhesion to concrete and other substrates. This is why epoxy flooring is often described as having adhesive-like bonding strength.
Because of this property, epoxy resin functions similarly to an Epoxy Adhesive, ensuring that the flooring system does not peel, crack, or delaminate under stress. The resin also contributes to surface smoothness, gloss retention, and abrasion resistance.
Compared to conventional cement-based flooring, epoxy resin-based systems offer superior resistance to chemicals, oils, and moisture. This chemical resilience extends the life of the flooring while reducing maintenance requirements, making epoxy flooring a cost-effective long-term solution.
Understanding Hardeners and Curing Agents
Hardeners are essential to epoxy flooring chemistry because they control how the resin transforms from a liquid into a solid. Different types of curing agents influence the final properties of the floor, including hardness, flexibility, and curing speed.
Amine-based hardeners are commonly used due to their strong cross-linking capability. The balance between resin and hardener is critical—too much or too little can compromise performance, leading to brittleness or incomplete curing.
The curing process directly affects the chemical stability of epoxy flooring. Properly cured systems achieve optimal mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. This highlights why accurate formulation and controlled application are essential for long-lasting epoxy flooring systems.
Additives, Fillers, and Pigments in Epoxy Flooring
Beyond resin and hardener, epoxy flooring formulations include additives, fillers, and pigments that enhance performance. Additives improve specific properties such as UV resistance, slip resistance, and flow control during application.
Fillers increase thickness, impact resistance, and load-bearing capacity. From a chemical standpoint, fillers also help control heat generation during curing and improve dimensional stability.
Pigments are chemically engineered to maintain color consistency and resist fading. These pigments are dispersed evenly at the molecular level, ensuring uniform appearance without compromising structural integrity.
Through chemical customization, epoxy flooring systems can be tailored for specific environments, from high-traffic industrial spaces to decorative commercial interiors.
Chemical Bonding and Adhesion Mechanism
One of the defining features of epoxy flooring is its ability to chemically bond with concrete substrates. Unlike mechanical adhesion, which relies on surface roughness alone, epoxy flooring forms chemical bonds with hydroxyl groups present in concrete.
This chemical adhesion significantly reduces the risk of cracking, peeling, or moisture-related failures. The adhesive nature of epoxy reinforces its classification alongside advanced Epoxy Adhesive systems used in structural applications.
Because the bond occurs at a molecular level, epoxy flooring distributes stress evenly across the surface. This enhances crack resistance and improves overall structural performance, particularly in high-load environments.
Chemical Resistance Properties of Epoxy Flooring
Epoxy flooring is widely valued for its resistance to acids, alkalis, solvents, oils, and cleaning chemicals. This resistance originates from its tightly cross-linked polymer network, which limits chemical penetration.
The molecular structure prevents aggressive substances from breaking down the surface, making epoxy flooring ideal for harsh industrial environments. Over time, this chemical stability ensures consistent performance without degradation.
Long-term resistance also means fewer repairs, less downtime, and improved safety. These advantages explain why epoxy flooring is commonly specified for facilities where chemical exposure is unavoidable.
Relationship Between Epoxy Flooring and Epoxy Potting Chemistry
Epoxy flooring shares strong chemical similarities with epoxy potting systems used to protect electrical and industrial components. Both rely on the same resin-hardener chemistry to achieve durability and chemical stability.
The difference lies mainly in formulation viscosity and application thickness, not in core chemistry. This overlap highlights why expertise in epoxy chemistry is transferable across industries.
In industrial markets, Epoxy Potting Manufacturers in Pakistan often utilize similar resin systems for encapsulation and flooring applications. This shared chemistry reinforces the versatility and reliability of epoxy-based solutions.
Applications Across Industries Based on Chemical Composition
The chemical adaptability of epoxy flooring allows it to serve diverse industries. In pharmaceutical and laboratory environments, chemical resistance and hygiene are critical. Epoxy flooring meets these needs through its non-porous surface.
In process industries and manufacturing plants, epoxy flooring withstands heavy loads, chemical spills, and constant traffic. In building and construction projects, it enhances durability and moisture protection.
Agricultural and research facilities also benefit from epoxy flooring due to its weather resistance and ease of cleaning. The chemistry behind epoxy flooring enables consistent performance across these varied applications.
Tile Bonding and Epoxy-Based Adhesive Systems
Epoxy flooring chemistry is closely related to epoxy-based tile bonding materials. Both rely on strong chemical adhesion and polymer cross-linking for performance.
Compared to cement-based tile bonds, epoxy systems offer superior bonding strength, water resistance, and longevity. These properties are especially important in areas exposed to moisture and chemicals.
In construction markets, the relevance of a Tile Bond Manufacturer in Pakistan reflects growing demand for advanced epoxy-based adhesive systems. The same chemistry that strengthens epoxy flooring enhances tile adhesion and structural reliability.
Environmental and Safety Considerations in Epoxy Chemistry
Modern epoxy flooring systems increasingly focus on environmental responsibility. Advances in chemical formulation have led to low-VOC and reduced-emission products that meet safety expectations.
Energy-efficient curing processes and optimized formulations help minimize environmental impact without compromising performance. Compliance with international safety standards ensures safe handling and long-term use.
The evolution of epoxy chemistry demonstrates how performance and sustainability can coexist in modern flooring solutions.
Quality Control and Standards in Epoxy Flooring Systems
Consistent chemical composition is essential for reliable epoxy flooring performance. Strict quality control ensures correct resin-to-hardener ratios and uniform additive dispersion.
International testing benchmarks evaluate hardness, adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. These standards help ensure that epoxy flooring systems deliver predictable and long-lasting results.
Controlled formulations reduce the risk of failure and enhance confidence in epoxy flooring for critical applications.
Future Trends in Epoxy Flooring Chemistry
Ongoing polymer research continues to improve epoxy flooring systems. Smarter additives, enhanced curing agents, and bio-based components are shaping the future of epoxy chemistry.
Sustainability remains a key focus, with efforts to reduce environmental impact while maintaining performance. Custom chemical solutions tailored to specific industries are also gaining importance.
These trends reinforce epoxy flooring as a future-ready solution driven by advanced chemistry.
Conclusion: Why Chemical Composition Defines Epoxy Flooring Performance
The performance of epoxy flooring is defined by its chemical composition. From resin structure and curing agents to additives and fillers, every component contributes to durability, safety, and efficiency.
Understanding epoxy chemistry explains why epoxy flooring outperforms traditional systems in demanding environments. Its adhesive strength, chemical resistance, and adaptability make it a reliable long-term solution.
As industries continue to demand high-performance flooring, epoxy flooring remains a proven, chemistry-driven system built for the future.