The parotid gland plays a vital role in your daily life. It produces saliva, which helps with chewing, swallowing, and digestion. You might not think about it often, but when swelling or discomfort appears near your jaw or ear, it can raise concerns. In this blog, we will explain “What is parotid gland?” and discuss the different types of tumors that can form there, so you can better understand your options and when to seek medical advice.
Although the word tumor sounds alarming, not all parotid gland tumors are dangerous. Some grow slowly and stay harmless for years. Others need closer attention. Knowing the difference helps you feel informed, calm, and prepared to speak with your care team.
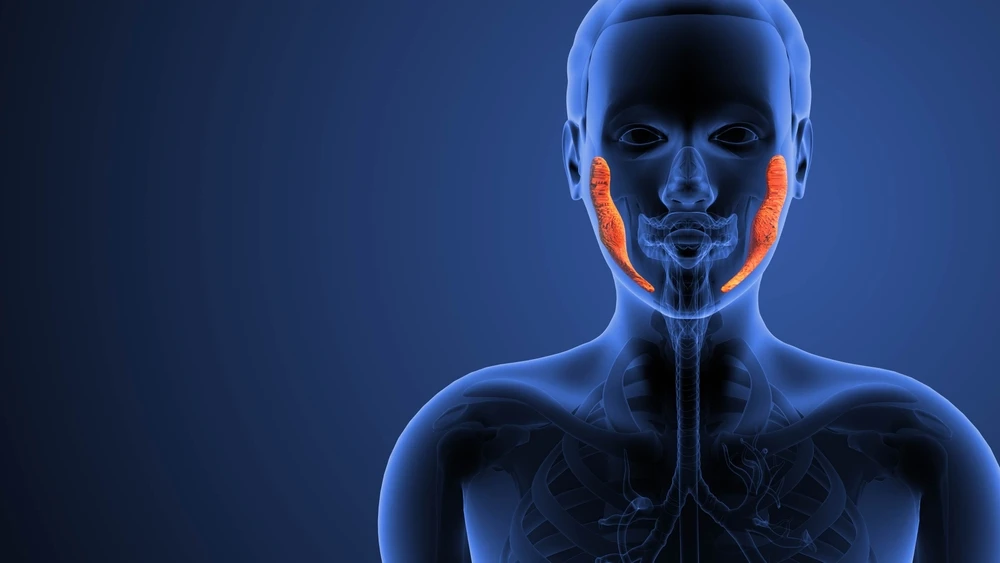
What Is the Parotid Gland and Why It Matters
The parotid gland plays a key role in daily oral function. It releases saliva through ducts into the mouth, especially when you eat. Without enough saliva, digestion becomes difficult and oral infections become more common.
In addition, the parotid gland sits close to important facial nerves. These nerves control facial movement and expression. Because of this location, even a small tumor can sometimes affect how your face feels or moves.
Key facts about the parotid gland include:
- It is the largest salivary gland
- It sits near the ear and jaw
- It helps protect oral health and digestion
Types of Parotid Gland Tumors
Parotid gland tumors fall into two main categories. They are either benign or malignant. Most tumors in this gland are benign. However, malignant tumors can be more aggressive and need timely care.
For example, a slow-growing lump that causes no pain often turns out to be benign. On the other hand, rapid changes or nerve symptoms may signal something more serious.
Benign Tumors
Benign tumors do not spread to other parts of the body. They usually grow slowly and may go unnoticed for months or even years. The most common benign tumor is pleomorphic adenoma. It often feels firm but painless. Another type, Warthin’s tumor, tends to appear in older adults and may affect both glands.
Although benign, these tumors still need attention. Over time, they can grow larger and press on nearby structures. Surgery is usually recommended to prevent future problems.
Common features of benign tumors include:
- Slow growth over time
- Minimal or no pain
- Very low risk of spreading
Malignant Tumors
Malignant parotid tumors are less common but more serious. These tumors are cancerous and can invade surrounding tissue. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is the most frequently diagnosed malignant type. Adenoid cystic carcinoma is another form known for spreading along nerves.
Symptoms may include facial weakness, numbness, or persistent pain. Because these tumors can behave aggressively, early diagnosis plays a critical role in treatment success.
Symptoms to Watch For
Parotid gland tumors do not always cause early symptoms. Still, there are warning signs you should not ignore.
- A lump or swelling near the jaw or ear
- Pain that does not go away
- Facial numbness or muscle weakness
- Difficulty opening the mouth fully
- Trouble swallowing
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical advice. Early evaluation can make treatment more effective.
Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Doctors use several tools to identify parotid gland tumors. First, they perform a physical exam. During this exam, they check the size of the lump and test facial nerve function.
Next, imaging tests help provide clearer details. Ultrasound is often used first. MRI or CT scans may follow to show the tumor’s exact location. In many cases, a biopsy is done. A fine needle is used to collect cells for examination.
Together, these tests help doctors understand the tumor type and plan the right treatment.
Some Treatment Options
Treatment depends on several factors. These include tumor type, size, and whether it has spread. Your overall health also matters.
Surgery
Surgery is the most common treatment option. It is used for both benign and malignant tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor while protecting the facial nerve. In skilled hands, nerve damage risk is reduced. Recovery varies depending on the procedure.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is often used after surgery for malignant tumors. It helps destroy remaining cancer cells. This approach lowers the chance of recurrence. Treatments are usually delivered over several weeks.
Clinical Trials and New Therapies
Some patients qualify for newer treatments through research studies. These trials explore targeted therapies and improved radiation methods. Participation may offer access to options not widely available yet.
Risk Factors and Prevention
There is no guaranteed way to prevent parotid gland tumors. However, certain factors may increase risk.
- Increasing age
- Prior exposure to radiation
- Family history of salivary gland tumors
Paying attention to symptoms and getting regular checkups improves early detection.
Living with a Parotid Gland Tumor
A diagnosis can feel overwhelming. Many patients worry about facial changes or long-term effects. Support from healthcare teams and loved ones is important. Follow-up visits help track recovery and catch any recurrence early.
Every patient’s journey is different. Some require only surgery, while others need combined therapies. Staying informed helps you feel more in control.
Conclusion
Parotid gland tumors range from harmless growths to serious cancers. Knowing the difference helps you respond quickly and wisely. Understanding symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options gives you a clearer path forward. At NHO Revive, we support patients by connecting them with research opportunities and expert guidance. If you want access to advanced treatment approaches, you can get enrolled in current solid tumor clinical trials through our platform.
By staying informed and seeking care early, you give yourself the best chance for positive outcomes. Visit NHO Revive and learn more about how we can support your journey.